Utilizing Multi-Core Modes#
Overview#
Mobilint NPU supports four core collaboration modes (hereafter referred to as core mode).
In user manual and tutorials, the Single mode - the most intuitive core mode - is primarily used to help understanding.
However, depending on the product you are using or the deep learning task you intend to perform, a different core mode may be more suitable.
Utilizing more appropriate core modes can provide significant performance improvements.
Currently, runtime library provides following core modes.
Important
Core modes are determined at the compilation stage. If you have already compiled MXQ, you cannot use core mode other than specified in your MXQ. You can figure out designated core mode in MXQ using mobilint-cli mxqtool.
To use your desired core mode, you must either
Compile the model directly with the desired mode, or
use an MXQ file that was compiled with desired mode.
Before getting started, it’s important to understand the overall internal architecture of the NPU.
Fundamentally, each core in the Mobilint NPU (referred to as a Local Core) can be regarded as the smallest unit capable of independently executing a single model.
These Local Cores are combined to form a Cluster.
Within each Cluster, there is an additional Global Core, which is responsible for coordinating tasks under the Multi/Global4,8 Modes. The Global Core manages the additional operations and communications required by these modes.
Please note that this internal architecture may vary depending on the Mobilint NPU product you are using. The structure can be illustrated as follows:
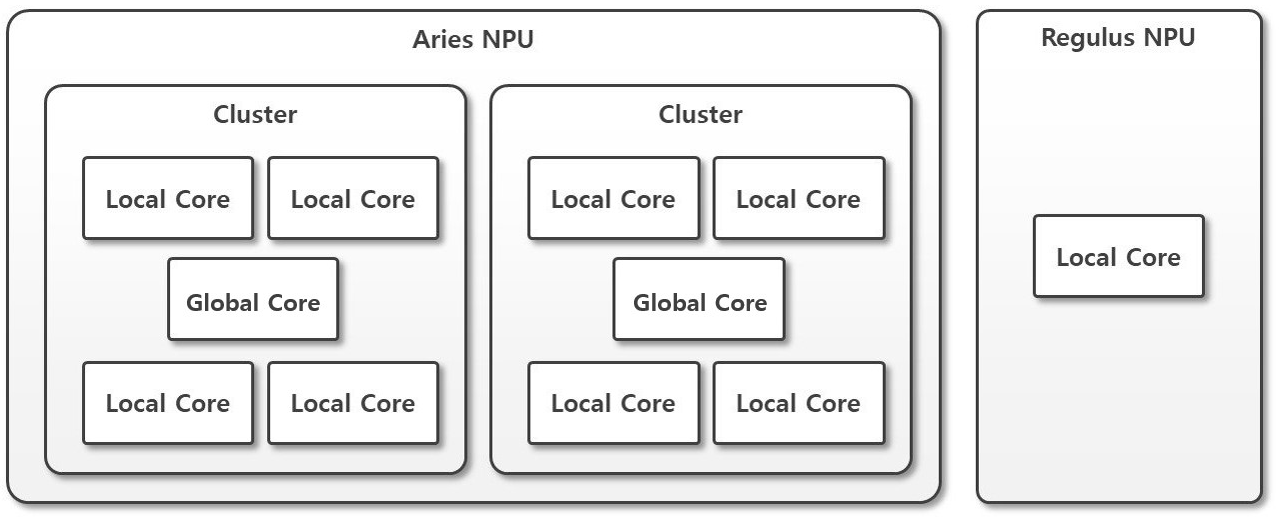
The available Core Modes differ depending on the Mobilint NPU products.
This variation is natural result of the internal architecture of each NPU product, specifically whether a Global Core is present or not. i.e. the REGULUS, which contains only a single Local Core, does not support Multi/Global4,8 Modes.
Product |
Single Mode |
Multi Mode |
Global4,8 Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
ARIES |
O |
O |
O |
REGULUS |
O |
X |
X |
From now on, the explanations of each Core Mode will be based on ARIES, a representative multi-core product.
Single Mode#
Single Mode is the most intuitive mode, where each Local Core operates independently.
In this mode, the user sends inference directly to individual cores and collects the results one by one to complete the desired task.
Since independent tasks can be executed across 8 cores, assigning work to all 8 cores continuously enables maximum performance (throughput).
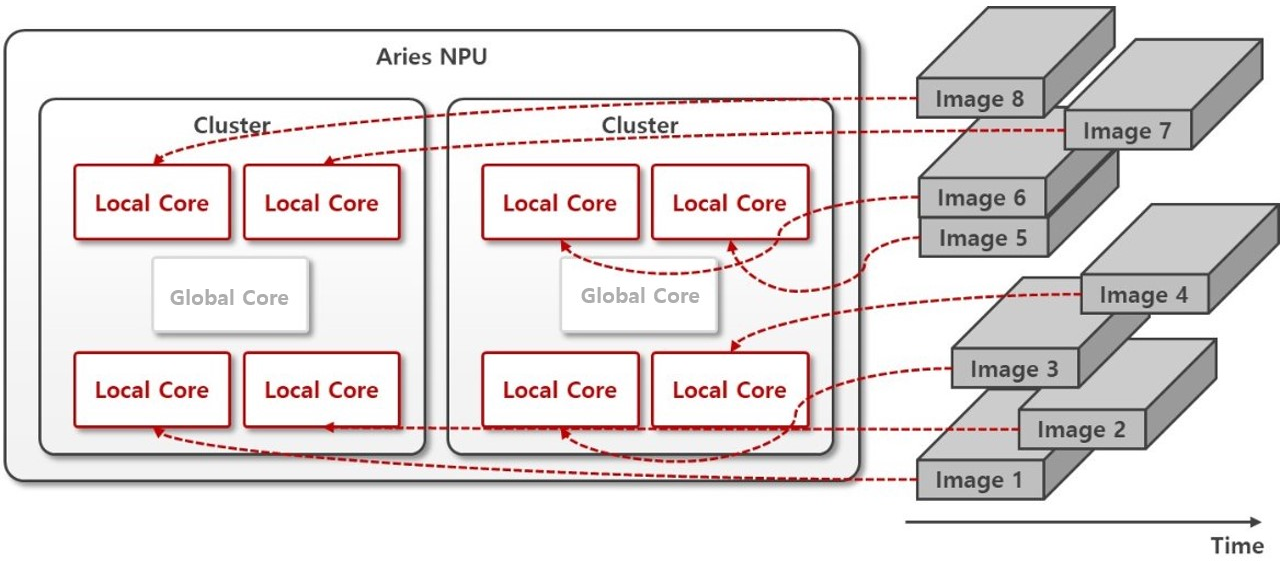
Note: While this mode is the most simple and intuitive for functional verification, it requires a mechanism that can send requests in non-blocking manner. Without a proper design - such as using multithreading or async I/O to send inference requests to multiple cores simultaneously - the system will fall back to fully sequential processing, resulting in wasting core utilization (utilizing only one core). Since multithreading and async I/O are common design patterns in software engineering, please refer to advanced usage or related resourses when designing them.
## Compilation stage
# Generate MXQ Model with Single-core Inference Scheme
from qubee import mxq_compile
mxq_compile(
...
inference_scheme="single" # Technically, this line can be omitted.
...
)
## Runtime stage with python
# Run Single-core Type Model
from maccel import Accelerator, Model, ModelConfig, CoreId, Cluster, Core
MXQ_PATH = "resnet50_single.mxq"
acc = Accelerator()
# Technically, these lines can be omitted - begin
mc = ModelConfig()
mc.set_single_core_mode(
core_ids=[
CoreId(Cluster.Cluster0, Core.Core0),
CoreId(Cluster.Cluster0, Core.Core1),
CoreId(Cluster.Cluster0, Core.Core3),
CoreId(Cluster.Cluster1, Core.Core2),
CoreId(Cluster.Cluster1, Core.Core3),
]
)
# end
model = Model(MXQ_PATH, mc) # If you omitted ModelConfig, erase the argument mc as well.
model.launch()
# model.infer(...)
// Runtime stage with C++
#include "maccel/maccel.h"
const char* MXQ_PATH = "resnet50_single.mxq";
int main() {
mobilint::StatusCode sc;
mobilint::ModelConfig mc;
auto acc = mobilint::Accelerator::create(sc);
if (!sc) exit(1);
if (!mc.setSingleCoreMode({
{mobilint::Cluster::Cluster0, mobilint::Core::Core0},
{mobilint::Cluster::Cluster0, mobilint::Core::Core1},
{mobilint::Cluster::Cluster0, mobilint::Core::Core3},
{mobilint::Cluster::Cluster1, mobilint::Core::Core2},
{mobilint::Cluster::Cluster1, mobilint::Core::Core3},
})) {
exit(1);
}
auto model = mobilint::Model::create(MXQ_PATH, mc, sc);
if (!sc) exit(1);
model->launch(*acc);
// auto result = model->infer();
}
Multi Mode#
This mode actually behaves as a batch processing mode, where multiple inputs are fed into the NPU at once, and multiple results are retrived from NPU together.
It operates at Cluster level, with each cluster consisting of 4 Local Cores.
Through coordination among the 4 Local Cores within a Cluster-managed by Global Core-the system performs operations optimized for 4-batch processing.

Use Cases
To struct the NPU inference logic in the same way as conventional batch processing
To achieve high performance(throughput) in 4-batch units without implementing multithreading or async I/O
## Compilation stage
# Generate MXQ Model with Multi-core Inference Scheme
from qubee import mxq_compile
mxq_compile(
...
inference_scheme="multi"
...
)
## Runtime stage with python
# Run Multi-core Type Model
from maccel import Accelerator, Model, ModelConfig, CoreId, Cluster, Core
MXQ_PATH = "resnet50_multi.mxq"
acc = Accelerator()
mc = ModelConfig()
mc.set_multi_core_mode([Cluster.Cluster0, Cluster.Cluster1])
model = Model(MXQ_PATH, mc)
model.launch()
# model.infer(...)
// Runtime stage with C++
#include "maccel/maccel.h"
const char* MXQ_PATH = "resnet50_multi.mxq";
int main() {
mobilint::StatusCode sc;
mobilint::ModelConfig mc;
auto acc = mobilint::Accelerator::create(sc);
if (!sc) exit(1);
if (!mc.setMultiCoreMode({
mobilint::Cluster::Cluster0,
mobilint::Cluster::Cluster1,
})) {
exit(1);
}
auto model = mobilint::Model::create(MXQ_PATH, mc, sc);
if (!sc) exit(1);
model->launch(*acc);
// auto result = model->infer();
}
Global Modes#
This is an inference method in which multiple cores work collaboratively to process a single piece of data.
For example, in the case of large and computationally heavy model, splitting the single input data across cores can potentially provide performance benefit in terms of latency.
Global Mode operates by utilizing Local Cores within a cluster, and is offered under the names Global4 Mode and Global8 Mode.
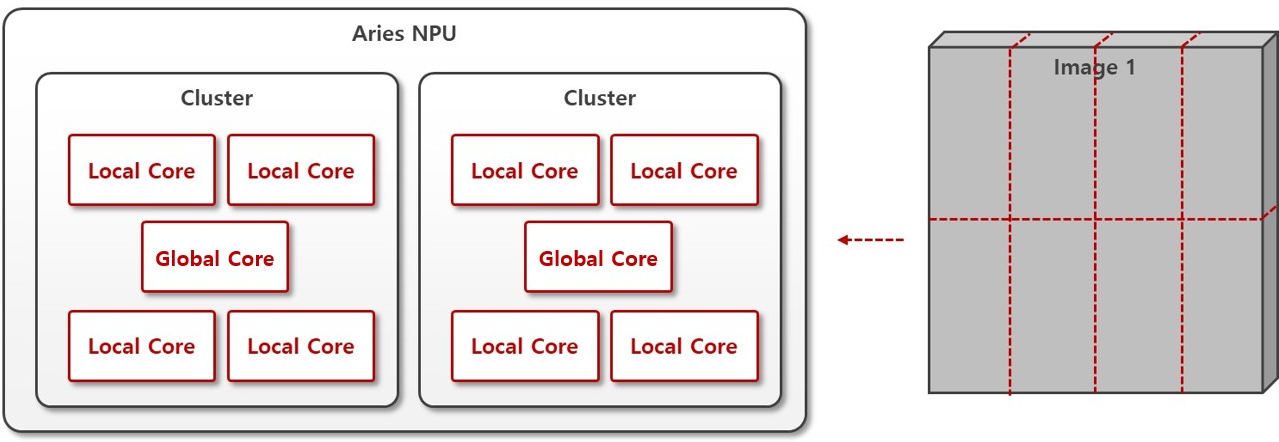
Use Cases
To reduce latency in large model.
Global4 Mode#
4 Local Cores (one Cluster) work together to process a single piece of data. You can freely select which Cluster to execute. Compilation and execution can be performed as shown in examples below:
## Compilation stage
# Generate MXQ Model with Global4 Inference Scheme
from qubee import mxq_compile
mxq_compile(
...
inference_scheme="global4"
...
)
## Runtime stage with python
# Run Global4 Type Model
from maccel import Accelerator, Model, ModelConfig, CoreId, Cluster, Core
MXQ_PATH = "resnet50_global4.mxq"
acc = Accelerator()
mc = ModelConfig()
mc.set_global4_core_mode([Cluster.Cluster1])
model = Model(MXQ_PATH, mc)
model.launch()
# model.infer(...)
// Runtime stage with C++
#include "maccel/maccel.h"
const char* MXQ_PATH = "resnet50_global4.mxq";
int main() {
mobilint::StatusCode sc;
mobilint::ModelConfig mc;
auto acc = mobilint::Accelerator::create(sc);
if (!sc) exit(1);
if (!mc.setGlobal4CoreMode({
mobilint::Cluster::Cluster1,
})) {
exit(1);
}
auto model = mobilint::Model::create(MXQ_PATH, mc, sc);
if (!sc) exit(1);
model->launch(*acc);
// auto result = model->infer();
}
Global8 Mode#
8 Local Cores (2 Clusters) work together to process a single piece of data. Compilation and execution can be performed as shown in the examples below:
## Compilation stage
# Generate MXQ Model with Global8 Inference Scheme
from qubee import mxq_compile
mxq_compile(
...
inference_scheme="global8"
...
)
## Runtime stage with python
# Run Global8 Type Model
from maccel import Accelerator, Model, ModelConfig, CoreId, Cluster, Core
MXQ_PATH = "resnet50_global8.mxq"
acc = Accelerator()
mc = ModelConfig()
mc.set_global8_core_mode()
model = Model(MXQ_PATH, mc)
model.launch()
# model.infer(...)
// Runtime stage with C++
#include "maccel/maccel.h"
const char* MXQ_PATH = "resnet50_global8.mxq";
int main() {
mobilint::StatusCode sc;
mobilint::ModelConfig mc;
auto acc = mobilint::Accelerator::create(sc);
if (!sc) exit(1);
if (!mc.setGlobal8CoreMode()) {
exit(1);
}
auto model = mobilint::Model::create(MXQ_PATH, mc, sc);
if (!sc) exit(1);
model->launch(*acc);
// auto result = model->infer();
}